Several states have existing laws that require insurance & Medicaid coverage of hearing aids.
-
State Insurance Coverage
-
State Medicaid Coverage
<
>
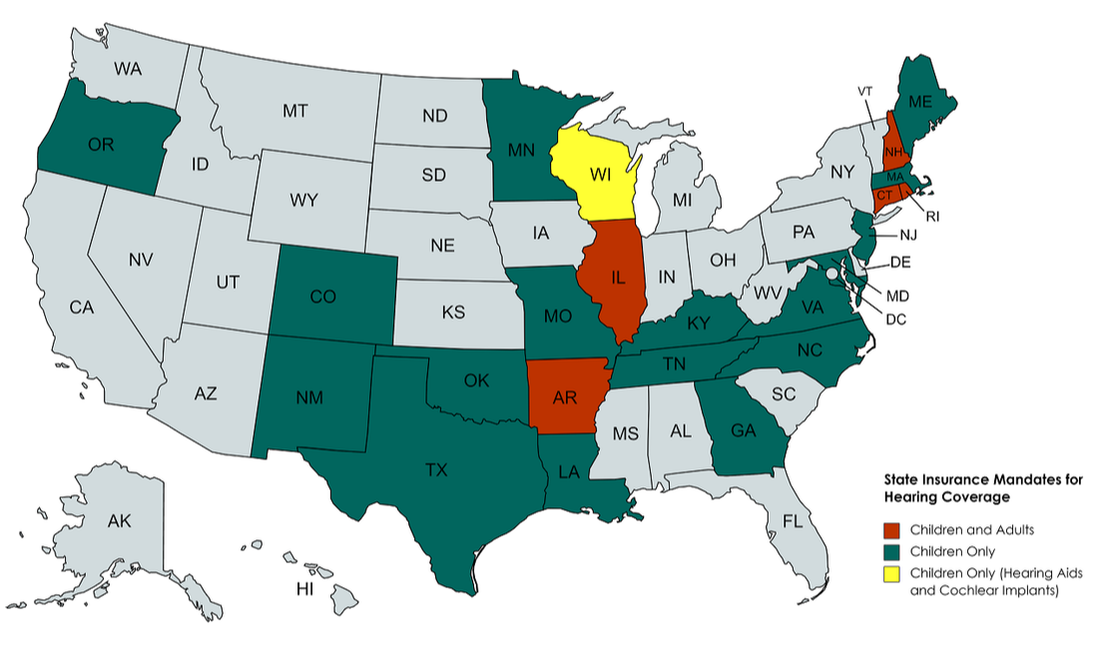
Currently, five states (AR, CT, IL, RI, & NH) have laws on the books that mandate insurance coverage of hearing aids for both children and adults. 18 states (CO, DE, GA, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MN, MO, NJ, NM, NC, OK, OR, TN, TX, VA) require that plans cover hearing aids for children only. One state (WI) requires coverage for both hearing aids and cochlear implants for children only. Requirements vary by state for: (1) ages covered; (2) the amount of coverage; (3) the benefit period; and (4) provider qualification.
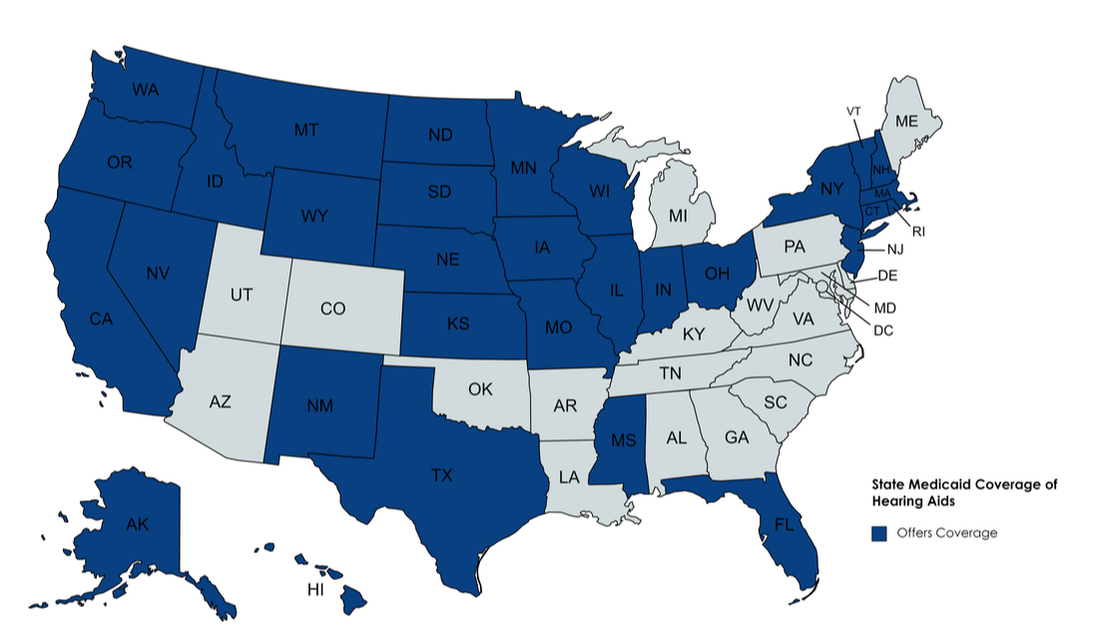
A majority of State Medicaid programs offer some form of coverage for hearing aids and related services to eligible recipients. However, statutes vary from state-to-state, and are subject to change given the fact that states often make revisions to the scope of Medicaid benefits. The Early and Periodic Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment Program (EPSDT) ensures that medically necessary audiological services, as well as hearing aids, are covered for beneficiaries under the age of 21 by all states.
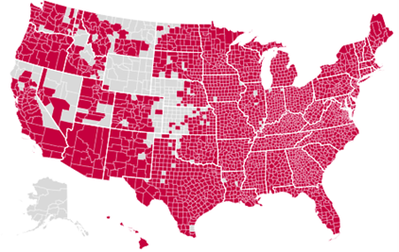
FACT SHEET: Medicare Advantage Hearing Coverage
|
A Kaiser Foundation analysis found that in 2020, 72 percent of MA enrollees participated in a plan that covered hearing aids (as compared to only 37 percent in 2010). In March 2020, over 17.6 million Medicare beneficiaries were enrolled in an MA plan covering aids and those that weren’t had options.
|
The Bottom Line: MA plans have been responsive to the demand for hearing aid benefits, and now access to hearing aid coverage is nearly universal for Medicare beneficiaries.